Technologies of CLST
Analysis of protein-crosslinking activity in the nucleus
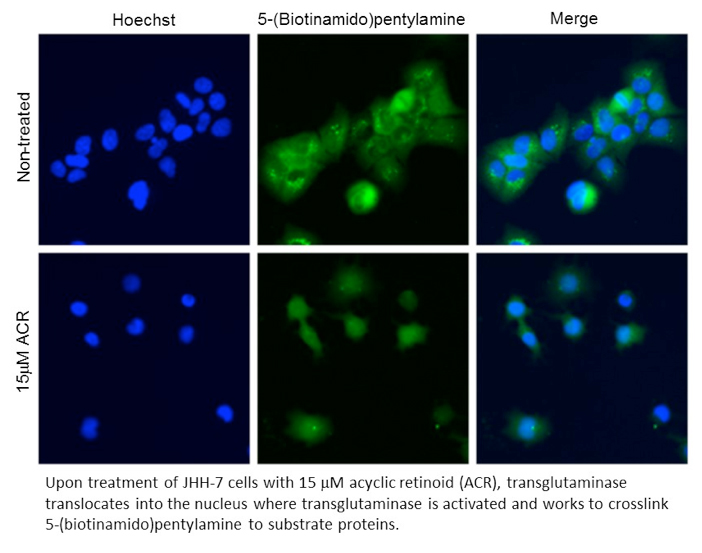
Transglutaminases covalently crosslink proteins between Lys and Gln residues. Various substrates have been reported, they are localized in the cytosol, nucleus, and extracellular region. Transglutaminase 2 has both nuclear import and export signals, and then transglutaminase 2 is accumulated in the nucleus and activated after treatment of the cells with ethanol, acyclic retinoid, and so on. Apoptosis is induced after crosslinking and silencing of a transcription factor Sp1 in the nucleus. Thus, detection of transglutaminase activity in the nucleus is important to assess cell fates. To this end, we have developed a new method to measure nuclear transglutaminase activity.
Method
After treatment of cultured cells with ethanol or acyclic retinoid, tranaglutaminase is accumulated in the nucleus and activated. To detect activated transglutaminase in the nucleus, a transglutaminase substrate, 5-(biotinamido)pentylamine, is added to the cells to allow substrate proteins to be crosslinked and labeled with 5-(biotinamido)pentylamine in the nucleus. Crosslinked 5-(biotinamido)pentylamine is detected by fluorescence-tagged streptavidin. Fluorescent images of the cells are collected and analyzed using an image analyzer (Image Express, Molecular Device).
References
- Free fatty acids induce transglutaminase 2-dependent apoptosis in hepatocytes via ER stress-stimulated PERK pathways. Kuo, T.F. et al. Journal of cellular physiology 227, 1130-1137 PMID:21567402 (2012).
- Role of transglutaminase 2 in liver injury via cross-linking and silencing of transcription factor Sp1. Tatsukawa, H. et al. Gastroenterology 136, 1783-1795 e1710 PMID:19208340 (2009)